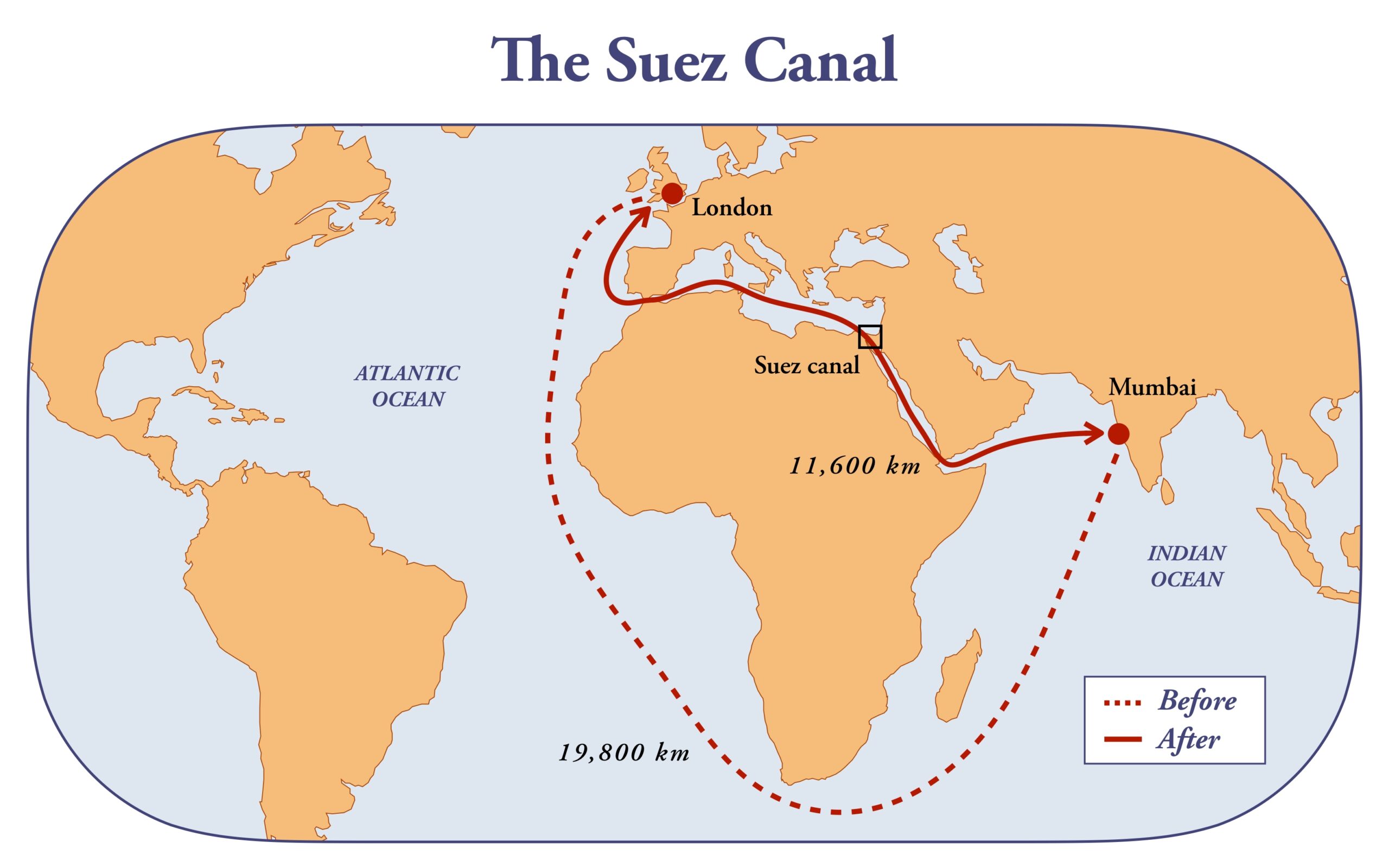
The ongoing conflict in the Bab al-Mandab Strait, situated between Yemen and Djibouti, holds far-reaching implications, particularly for the adjacent Suez Canal. This article provides a detailed exploration of the historical significance of the Suez Canal, its profound impact on global trade, the challenges it faces, and the broader economic implications of the current Red Sea conflict.
Historical Significance of the Suez Canal:
The Suez Canal and the Panama Canal, recognized as monumental achievements in logistics, have redefined maritime trade by connecting continents and significantly reducing travel time for vessels. With its construction completed in 1869, the Suez Canal boasts a rich history dating back almost 3000 years when it facilitated trade between the Nile River Delta and the Red Sea.
Closures and Open Passage Policy:
The Suez Canal, despite the establishment of the open passage policy in 1888 which reflected a global commitment to keeping the canal accessible to ships of all nations during both peacetime and war, has experienced closures during major global events. These global events include WWI, WWII, the Suez Crisis of 1956-57, and the Arab Israeli War of 1967. More recent incidents, such as the six-day obstruction in 2021 caused by a 224,000-ton vessel which was rotated due to high winds and remained stuck for 6 days, underscore the vulnerability of this critical waterway resulting in hundreds of millions of dollars in damages.
Recent Incidents and Vulnerabilities:
The current Red Sea dispute involves Houthi rebels launching numerous attacks on vessels in the Red Sea, with over 25 vessels targeted since November 2023. These attacks include drone and missile strikes against commercial ships, a pattern that has become increasingly recurrent. Successful countermeasures have been undertaken by the USS Carney, a well-equipped U.S. Navy destroyer.
Houthi Attacks and Historical Context:
The Houthi regime’s attacks on vessels in the Suez Canal are part of a broader pattern, with periodic assaults on ships carrying medical supplies, weapons, and oil in response to conflicts between Saudi Arabia and the UAE. Backed by Iran, the Houthi rebels have demonstrated military upgrades and training, executing attacks with precision. Recent attacks have intensified as a direct result of the Gaza conflict, with the Houthi regime openly declaring their actions as a response to the war between Israel and Hamas. They claim to focus on ships with Israeli connections, whether owned, flagged, operated, or heading to Israeli ports although many of the ships attacked very clearly did not fall under any of those categories and in one circumstance a vessel clearly flew the Chinese flag.
Global Retaliation:
International response to these attacks involves direct retaliation, with the United States leading efforts. The justification for this retaliation is a direct response to the attacks on the Red Sea, “jeopardizing trade routes and threatening freedom of navigation” as stated by President Joe Biden.
Impact on Global Trade and Economies:
The economic consequences of these attacks are profound. 4 out of 5 of the major shipping companies (of whom handled 53% of the world’s trade) have redirected shipments away from the Red Sea, altering established trade routes and adding time and costs to transportation. Previously managing 12 percent of global trade, the Suez Canal’s redirection has led to increased oil prices, shipping costs, and war risk insurance premiums. This has contributed to a trickle of inflation in global markets. The six-day blockage in 2021 caused by the Ever Given resulted in billions of dollars in cargo coming to a halt and hundreds of millions in fines and there is no telling how dramatic the repercussions will be following this lengthy dispute.
Alternative Solutions and Economic Ramifications:
Alternative solutions, such as a heavy-duty train line from Europe to Asia and the Northern Sea Route between Russia and the North Pole, have been proposed to mitigate the impact of potential future disruptions. However, logistical challenges and skepticism regarding the viability of these alternatives pose uncertainties. The economic fallout extends beyond Egypt, where about 10 percent of their GDP relies on the Suez Canal, to other countries as well, considering the majority of targeted ships are not bound for Israel. The extended shipping times have caused an intense disruption to Australia as they previously received 16% of all of their shipments through the Red Sea.
Resolving the Issue:
Resolving the issue requires a delicate balance of diplomatic efforts, which seem challenging given escalating tensions, and the use of force, a more likely scenario. The extent of the impact on the global economy remains uncertain, demanding continuous vigilance.
What can you do next?
Remaining informed is imperative for organizations engaged in global trade. Mitigating risks and exploring alternative solutions will be critical in navigating uncertainties arising from the current conflict in the Red Sea region.
At BDG, we prioritize staying updated to provide effective and economical solutions to our clients, mitigating the effects on their transport. To explore how we can mitigate risk for your important freight, submit a form to our solutions team and join us on a no-obligation discovery call.
https://www.reuters.com/markets/commodities/how-are-red-sea-attacks-impacting-shipping-suez-canal-2023-12-18/
https://www.britannica.com/topic/Suez-Canal
https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2024/1/16/malta-flagged-cargo-ship-hit-by-missile-in-red-sea#:~:text=The%20Iran%2Dbacked%20Houthis%20have,to%20Israel’s%20bombardment%20of%20Gaza
https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2024/1/13/have-the-houthi-red-sea-attacks-hurt-israels-economy\
https://www.suezcanal.gov.eg/English/Navigation/Pages/NavigationStatistics.aspx
https://www.iwm.org.uk/history/why-was-the-suez-crisis-so-important#:~:text=The%20canal%20was%20closed%20to%20traffic%20for%20five%20months%20by,limited%20and%20resulted%20in%20shortages.
https://www.britannica.com/event/Suez-Crisis
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Suez_Canal#:~:text=Under%20the%20Anglo%2DEgyptian%20Treaty,remained%20closed%20to%20Axis%20shipping.
https://www.britannica.com/place/Egypt/The-revolution-and-the-Republic
https://www.britannica.com/event/Arab-Israeli-wars
https://www.economist.com/international/2023/12/16/a-new-suez-crisis-threatens-the-world-economy
https://www.bbc.com/news/world-middle-east-67614911
https://www.usni.org/magazines/proceedings/2021/may/suez-canal-and-global-trade-routes
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/2021_Suez_Canal_obstruction
https://www.iemed.org/publication/the-economic-impacts-of-the-new-suez-canal/#:~:text=It%20represents%20almost%205%25%20of,annually
https://www.economist.com/international/2023/12/16/a-new-suez-crisis-threatens-the-world-economy?utm_medium=cpc.adword.pd&utm_source=google&ppccampaignID=17210591673&ppcadID=&utm_campaign=a.22brand_pmax&utm_content=conversion.direct-response.anonymous&gad_source=1&gclid=CjwKCAiAkp6tBhB5EiwANTCx1DE6fh0XvUpPgWAl89FSME6rdfMIm-f-4eyzff7UxCEe5OZKLgvUFBoCsQUQAvD_BwE&gclsrc=aw.ds